43 if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is
if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time t what is ... Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time t what is the relationship between these quantities kumbhajchandrak1767 kumbhajchandrak1767 29.01.2018 CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 13 MCQ Objective of Motion ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is: [A]. S = D x T [B]. T = S/D [C]. S = 1 x D/ T [D]. S = T/D. View Answer; Q6 In a science quiz competition, Payel are asked a question where she had to choose the statement which was/were correct? ...
MCQ Motion and Time Chapter 13 Class 7 Science - eVidyarthi MCQ Motion and Time Chapter 13 Class 7 Science. 1. A bus travels 54 km in 90 minutes. The speed of the bus is. 2. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. 3. Observe the figure given below: 4.
If we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is
If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T the ... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T the relationship these equation is? Solve Study Textbooks Guides. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Physics >> Motion in a Straight Line >> Speed and Velocity >> If we denote speed by S , distance by D . 10. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is taniya4486 taniya4486 29.05.2020 Physics Secondary School answered 10. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is 2 See answers If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. Sign Up. Sign Up to our social questions and Answers Engine to ask questions, answer people's questions, and connect with other people.
If we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is. NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time ... (b) 10 m/s (c) 5.4 m/s (d) 3.6 m/s Answer: (b) As, we know that. Question 5: If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is Answer: (c) The correct relationship is. Question 6: Observe the given figure. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and ... If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T ... Find an answer to your question If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is * sairsawant15 sairsawant15 2 weeks ago Physics Primary School answered If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is * 2 See answers ... Speed, Time, Distance| Rules & Tricks| Quantitative ... Time taken = x-10 As the Distance traveled is the same, the ratio of Speed in case 1 to the Speed in case 2 will be the inverse of the Time taken in both cases Ratio of Speed in both cases = 4:6 = 2:3 Ratio of Time in both cases = 3:2 Therefore (x+20)/(x-10)=3/2 2x+40 = 3x -30 x= 70 minutes Taking case 1, 4= d/(90/60)=> d= 360/60 = 6 km Distance, speed and time formulae - Distance, Speed and ... An easy way to remember the formulae is to put distance, speed and time (or the letters D, S and T) into a triangle. The triangles will help you remember these three rules: \[Distance = Speed ...
Speed, Distance and Time Formula: Definition and Solved ... The speed distance time formula explains the relationship between these three variables. ... speed of an object refers to the distance travelled divided by time and it expressed as : Speed = distance/time. s = d/t. ... Speed distance time formula is given as x =d/t. Substituting the values, we get. Distance = 50/2.5 = 125km. Hence, the car can ... Class 7 Important Questions for Science - Motion and Time If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S / D (c) S = 1 / T * D (d) S = T / D; Observe Figure 13.3. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A. NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time ... If we denote speed by 5, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S=D × T (b) T=S/D (c) S=1/T x D (d) S=T/D Solution: (c) Question 6. Observe figure. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A. Distance/Speed Relation: Velocity Formula and Practice ... The speed is the time rate of change of the distance. If 'D' is the distance of an object in some time 'T', the speed is equal to, s = D/T. It has the same units as velocity. let us solve some examples, we will introduce the formulae as we go along. Examples. Example 1: The speed of a bus is 54 km/h if we don't let it stop at any point.
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is * * (a) S = D/ T (b) T = SD (c) S = 1T × D (d) S = TD 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement RamArora RamArora Answer: a)S=D/T is the correct answer for sure . Explanation: NCERT Exemplar solutions for Class 7 Science ... - BYJUS Speed = Distance / Time. Distance = 54km = 54 x1000 = 54000m. Time = 90 minutes = 90×60= 5400s. Speed = 54000/5400 = 10 m/s. 5. If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. (PDF) Solved problems in modern physics - Academia.edu i love physics. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Question 5 If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time ... Question 5 If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities isa S=D Tb T = S / Dc S =1/ T × Dd S=1/D
If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T ... If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S/D (c) S = 1/TxD (c) S = T/D - Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for students.
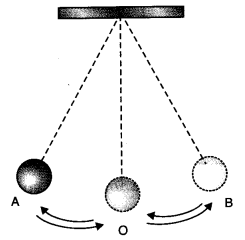
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time If we denote speed by 5, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S=D × T (b) T=S/D (c) S=1/T x D (d) S=T/D Solution: (c) Question 6. Observe figure. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A.
MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 ... - Learn Insta If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D T (b) T = \(\frac{S}{D}\) (c) S = \(\frac{1}{T}\) × D (d) S = \(\frac{T}{D}\) ... We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries ...
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is :a. S=D… Get the answers you need, now! sworldwidehr sworldwidehr 18.05.2020 Science Secondary School answered If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is : a. S=D ×T
How Are Speed, Distance and Time Related? - Reference.com The relationship for speed is the same for any units, as long as the units are consistent. If a car traveled 30 miles in an hour, the speed would be 30 miles per hour. If an object is moving at varying speeds, then the relationship between speed, distance and time can only be used to calculate the average speed.
Formula of Speed Time and Travelled Distance - VEDANTU The speed of a moving object can be calculated as: Speed =. D i s t a n c e T i m e. Speed can either be uniform or variable. Average Speed: The average speed is the total distance covered by an object in a particular interval of time. For example, If a moving object covers d₁, d₂, d₃...dₙ with different speed V₁, V₂, V₃ m/s in ...
› topics › engineeringSignificant Wave Height - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Measurements with high σ 0 correspond to times of low wind speed (σ 0 = 13 dB ⇔ U 10 ≈ 4 m s −1) or, equivalently, swell conditions.Since the period algorithm is based on H s alone when σ 0 > δ, this gives a model in which all swell has the same steepness for a given H s.
courses.lumenlearning.com › physics › chapterPhysical Quantities and Units | Physics - Lumen Learning Suppose that you drive the 10.0 km from your university to home in 20.0 min. Calculate your average speed (a) in kilometers per hour (km/h) and (b) in meters per second (m/s). (Note: Average speed is distance traveled divided by time of travel.) Strategy. First we calculate the average speed using the given units.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Distance_measures_(cosmology)Distance measures (cosmology) - Wikipedia Distance measures are used in physical cosmology to give a natural notion of the distance between two objects or events in the universe.They are often used to tie some observable quantity (such as the luminosity of a distant quasar, the redshift of a distant galaxy, or the angular size of the acoustic peaks in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) power spectrum) to another quantity that is ...
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is ... Unanswered; Ask a Question; Learn; Ask a Question. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is ... asked Jan 23, 2018 in Science by Rohit Singh (65.1k points) If we denote speed by S ...
If We Denote Speed By S, Distance By D And Time By T, The ... Class 7 Science / MCQs on Motion and Time Choose an option to see the answer | Answer another question | Take a practice test If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is\r\n
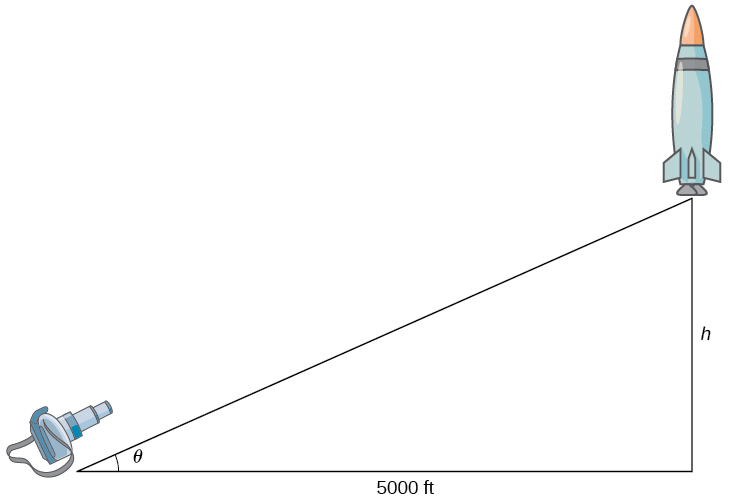
4.1 Related Rates - Calculus Volume 1 - OpenStax Since we are asked to find the rate of change in the distance between the man and the plane when the plane is directly above the radio tower, we need to find d s / d t d s / d t when x = 3000 ft. x = 3000 ft. Step 3. From the figure, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to write an equation relating x x and s: s:
Motion and Time Class 7 Extra Questions ... - Learn CBSE If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these Quantities is [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (d) \(S=\frac{1}{T} \times D\) Question 6. Which one records the distance travelled by a vehicle? (a) Speedometer (b) Manometer (c) Motometer (d) Odometer Answer: (d) Odometer. Question 7.
PDF Motion and Time - NCERT (a) 0.6 m/s (b) 10 m/s (c) 5.4 m/s (d) 3.6 m/s 5. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S D (c) S = 1 D T × (d) S = T D 6. Observe Figure 13.3. Fig 13.3 The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A. (b) O ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Special_relativitySpecial relativity - Wikipedia where v(t) is the velocity at a time t, a is the acceleration of 1g and t is the time as measured by people on Earth. Therefore, after one year of accelerating at 9.81 m/s 2, the spaceship will be travelling at v = 0.77c relative to Earth. Time dilation will increase the traveller's life span as seen from the reference frame of the Earth to 2.7 ...
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is. Sign Up. Sign Up to our social questions and Answers Engine to ask questions, answer people's questions, and connect with other people.
10. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is taniya4486 taniya4486 29.05.2020 Physics Secondary School answered 10. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is 2 See answers
If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T the ... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T the relationship these equation is? Solve Study Textbooks Guides. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Physics >> Motion in a Straight Line >> Speed and Velocity >> If we denote speed by S , distance by D .

























0 Response to "43 if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is"
Post a Comment